文章内容
自定义注解,项目启动时进行注解扫描并存储,便于后面生成对象。类似于@Controller,@Service,自定义的原因是,整个项目会初始化很多流程,每个流程由好多个小模块(对象)串联起来。同一个类会被创建多个对象,被使用在不同的流程里面。以后会根据流程的配置对应切换对象。
1、项目结构
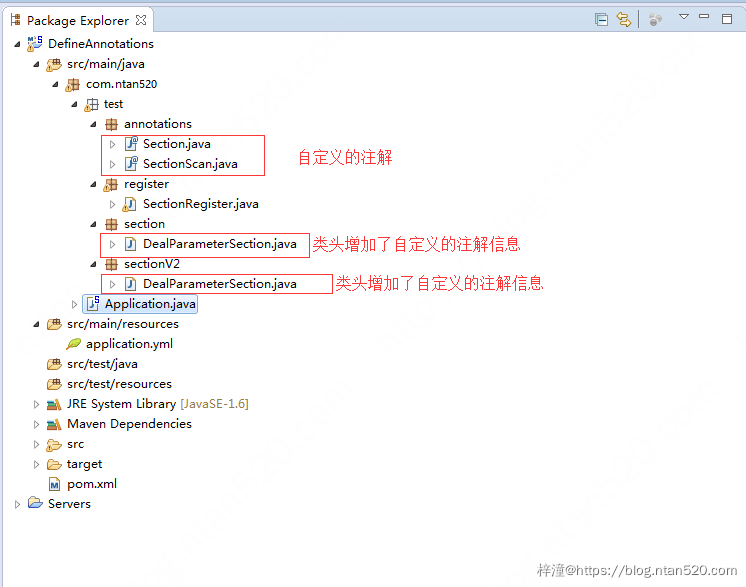
2、pom.xml依赖添加
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
3、配置文件application.yml
server:
port: 8083
4、注解类定义
/**
* 在类上面写 @Section(id = "xxx", remark = "xxx")
* 类似于@Controller的使用
*/@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
public @interface Section {
String id();
String remark();
String v() default "1";
}
/**
* 启动类上面@SectionScan(basePackages={"扫描的类路径"})
* 类似@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.ntan520.*"})
*/@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Import({SectionRegister.class})
public @interface SectionScan {
String[] basePackages() default {};
}
5、启动类
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = {"com.ntan520.*"}) // springboot 扫描指定包下面的注解
@SectionScan(basePackages={"com.ntan520.test.section.*","com.ntan520.test.sectionV2.*"}) // 扫描2个指定包的下的注解
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
6、被扫描的类
@Section(id = "dealParameter", remark = "参数处理")
public class DealParameterSection {
}
7、注册类
public class SectionRegister
implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware, EnvironmentAware {
Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(SectionRegister.class);
private static Map<String, Section> SECTION_MAP = new HashMap<String, Section>();
private ResourceLoader resourceLoader;
private ClassLoader classLoader;
private Environment environment;
public void setSectionMap(Map<String, Section> sectionMap) {
SECTION_MAP = sectionMap;
}
public void setEnvironment(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
}
public void setBeanClassLoader(ClassLoader classLoader) {
this.classLoader = classLoader;
}
public void setResourceLoader(ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
}
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
logPackageScan(importingClassMetadata);
registerSections(importingClassMetadata, registry);
}
private void logPackageScan(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
Map<String, Object> defaultAttrs = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(SectionScan.class.getName(), true);
if (defaultAttrs != null && defaultAttrs.size() > 0) {
LOG.info("section package scan: " + buildPackages((String[]) defaultAttrs.get("basePackages")));
}
}
private String buildPackages(String[] basePackages) {
if (basePackages == null || basePackages.length == 0) {
return "null";
}
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (String s : basePackages) {
stringBuilder.append(s).append(",");
}
stringBuilder.substring(0, stringBuilder.length() - 2);
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
public void registerSections(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider scanner = getScanner();
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.resourceLoader);
Map<String, Object> attrs = metadata.getAnnotationAttributes(SectionScan.class.getName());
AnnotationTypeFilter annotationTypeFilter = new AnnotationTypeFilter(Section.class);
scanner.addIncludeFilter(annotationTypeFilter);
Set<String> basePackages = getBasePackages(metadata);
Map<String, Section> sectionMap = new HashMap<String, Section>();
for (String basePackage : basePackages) {
Set<BeanDefinition> candidates = new LinkedHashSet<BeanDefinition>();
ResourcePatternResolver resourcePatternResolver = new PathMatchingResourcePatternResolver();
try {
// 这里特别注意一下类路径必须这样写
// 获取指定包下的所有类
basePackage = basePackage.replace(".", "/");
Resource[] resources = resourcePatternResolver.getResources("classpath*:" + basePackage);
MetadataReaderFactory metadata1 = new SimpleMetadataReaderFactory();
for (Resource resource : resources) {
MetadataReader metadataReader = metadata1.getMetadataReader(resource);
ScannedGenericBeanDefinition sbd = new ScannedGenericBeanDefinition(metadataReader);
sbd.setResource(resource);
sbd.setSource(resource);
candidates.add(sbd);
}
for (BeanDefinition beanDefinition : candidates) {
String classname = beanDefinition.getBeanClassName();
// 扫描Section注解
Section s = Class.forName(classname).getAnnotation(Section.class);
if (s != null) {
sectionMap.put(classname, s);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//使用容器存储扫描出来的对象(类全限定名:section对象)
setSectionMap(sectionMap);
}
protected ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider getScanner() {
return new ClassPathScanningCandidateComponentProvider(false, this.environment) {
@Override
protected boolean isCandidateComponent(AnnotatedBeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
if (beanDefinition.getMetadata().isIndependent()) {
if (beanDefinition.getMetadata().isInterface()
&& beanDefinition.getMetadata().getInterfaceNames().length == 1
&& Annotation.class.getName().equals(beanDefinition.getMetadata().getInterfaceNames()[0])) {
try {
Class<?> target = ClassUtils.forName(beanDefinition.getMetadata().getClassName(),
SectionRegister.this.classLoader);
return !target.isAnnotation();
} catch (Exception ex) {
this.logger.error(
"Could not load target class: " + beanDefinition.getMetadata().getClassName(), ex);
}
}
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
}
protected Set<String> getBasePackages(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata) {
Map<String, Object> attributes = importingClassMetadata
.getAnnotationAttributes(SectionScan.class.getCanonicalName());
Set<String> basePackages = new HashSet<String>();
for (String pkg : (String[]) attributes.get("basePackages")) {
if (pkg != null && !"".equals(pkg)) {
basePackages.add(pkg);
}
}
if (basePackages.isEmpty()) {
basePackages.add(ClassUtils.getPackageName(importingClassMetadata.getClassName()));
}
return basePackages;
}
}
8、总结
- 项目启动后,会自动扫描指定包下面带有@Section注解的类,放入到Map中,key是全限定性包名,value是一个Section对象(包含id属性值,remark备注,v版本号)
- Map内容如下:{com.ntan520.test.sectionV2.DealParameterSection=@com.ntan520.test.annotations.Section(v=2, id=dealParameter.2, remark=参数处理), com.ntan520.test.section.DealParameterSection=@com.ntan520.test.annotations.Section(v=1, id=dealParameter, remark=参数处理)}
- 将Map重新整理成为一个Map,把value中的id作为新key,其余属性重新封装到SectionConfigObj对象中。
- 初始化的时候会读取流程配置的id名(可替换),从Map中获得SectionConfigObj对象放入流程里
