文章内容
一、css布局简介
布局在我们前端日常开发来说是非常重要的,一个好的布局能简化代码的同时还能提高网页的性能。常见的布局方法有:
浮动(float)布局、绝对定位(position)布局、表格布局(table)、弹性(flex)布局、网格(grid)布局
本文主要讲解水平垂直居中、单栏布局、双栏布局、三栏布局一些项目中常用的布局方案。

二、居中
居中在我们日常工作中还是会经常碰到。
1、水平居中
对于水平居中一般可以使用如下四种方式:
- 1. 对于行内元素我们可以在父元素上设置text-align:center;来实现。
- 2. 对于定长块级元素我们可以使用margin: 0 auto;来实现。
- 3. 我们可以在父元素上使用flex布局来实现。
- 4. 我们可以在父元素上使用grid布局来实现。
1)html
<div class="div1">
<span>行内元素水平居中</span>
</div>
<div class="div2">
<span>行内元素水平居中</span>
<div>块级元素水平居中</div>
</div>
<div class="div3">
<span>行内元素水平居中</span>
<div>块级元素水平居中</div>
</div>
<div class="div4">块级元素水平居中</div>
2)css
.div1 {
text-align: center;
}
.div2 {
display: flex;
justify-content: center;
}
.div3 {
display: grid;
justify-content: center;
}
.div4 {
width: 130px;
margin: 0 auto;
}
3)效果图

2、垂直居中
对于垂直居中一般可以使用如下三种方式:
- 1. 我们可以在父元素上设置line-height等于height来实现。
- 2. 我们可以在父元素上使用flex布局来实现。
- 3. 我们可以在父元素上使用grid布局来实现。
- 4. 我们可以在父元素上使用table布局来实现。
1)html
<div class="div1">
<span>行内元素垂直居中</span>
<!-- <div>块级元素垂直居中</div> -->
</div>
<div class="div2">
<span>行内元素垂直居中</span>
<div>块级元素垂直居中</div>
</div>
<div class="div3">
<span>行内元素垂直居中</span>
<div>块级元素垂直居中</div>
</div>
<div class="div4">
<span>行内元素垂直居中</span>
<div>块级元素垂直居中</div>
</div>
2)css
.div1 {
height: 100px;
background: lightgreen;
line-height: 100px;
}
.div2 {
height: 100px;
background: lightblue;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
}
.div3 {
height: 100px;
background: lightgreen;
display: grid;
align-content: center;
}
.div4 {
height: 100px;
background: lightblue;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
3)效果图
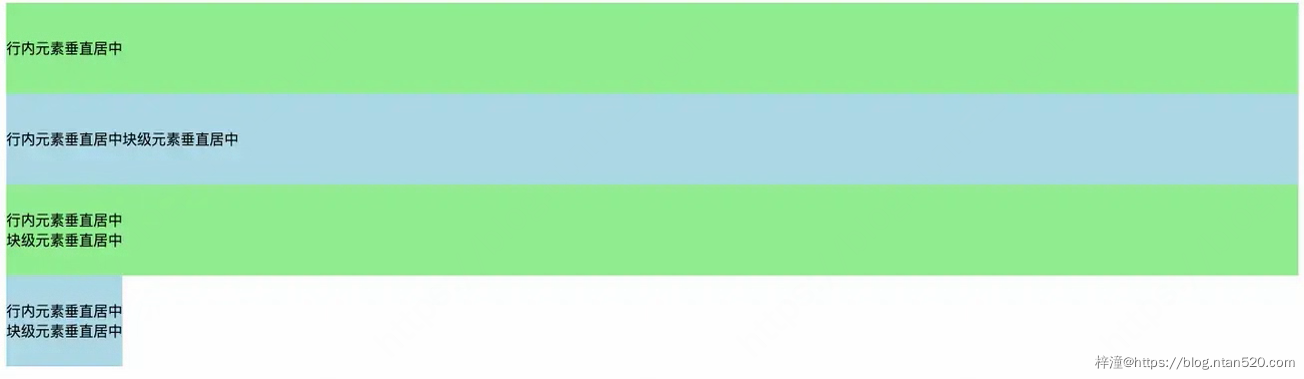
3、水平垂直同时居中
比如我们想实现如下水平垂直同时居中的效果:

实现水平垂直同时居中我们可以使用绝对定位、table布局、flex布局 或 grid布局来实现。
首先我们创建一个需要居中的盒子。
<div class="box"></div>
1)纯绝对定位
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
top: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin: auto;
}
2)绝对定位加负外边距
这种方式需要知道居中元素的具体宽高,不然负的margin没法设置。
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
margin-left: -100px;
margin-top: -50px;
}
3)绝对定位加平移
这种平移的方式就不需要考虑居中盒子的具体宽高了。
.box {
position: absolute;
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
left: 50%;
top: 50%;
transform: translate(-50%, -50%);
}
4)使用flex实现
html,body {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background: gray;
display: flex;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
}
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
}
5)使用grid实现
html,body {
height: 100%;
}
body {
background: gray;
display: grid;
/* align-content: center;
justify-content: center; */
/* align-content和justify-content的简写 */ place-content: center;
}
.box {
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
background: red;
}
6)使用table加外边距实现
使用table布局需要注意如下:
- display: table时padding会失效
- display: table-row时margin、padding同时失效
- display: table-cell时margin会失效
<div class="box">
<div class="child"></div>
</div>
.box {
background: red;
height: 300px;
width: 600px;
display: table-cell;
vertical-align: middle;
}
.child {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background: lightgreen;
margin: 0 auto;
}
三、单栏布局
单栏布局我们常用在网页框架上,一般我们把网页分为 header、content、footer三部分。

在不同的项目我们可能对这三部分的样式需求有所差别,比如需要顶部固定、需要底部固定等等。
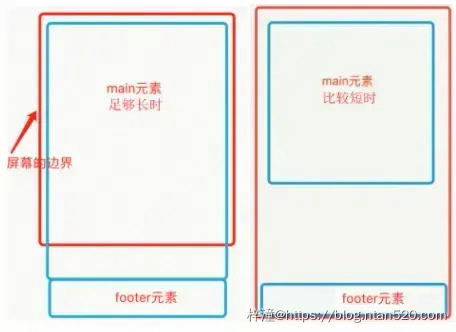
1、顶底部都不固定
比如想实现如下效果,footer在内容不足的时候吸附在窗口底部,当内容多的时候又可以被抵到窗口下面。
1)使用padding加负margin实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
min-height: 100%;
padding-bottom: 50px;
overflow: auto;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ height: 100px;
/* height: 1000px; */}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
margin-top: -50px;
}
2)使用flex实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
min-height: 100%;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ height: 100px;
/* height: 1000px; */ flex-grow: 1;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
}
2、顶部固定
1)使用padding加负margin加fixed实现顶部固定布局
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="wrap">
<div class="content">content</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.wrap {
min-height: 100%;
padding-bottom: 50px;
overflow: auto;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.content {
margin-top: 50px;
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ height: 100px;
/* height: 1000px; */}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
margin-top: -50px;
}
2)使用flex加fixed定位实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
min-height: 100%;
flex-direction:column;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ /* height: 100px; */ height: 1000px;
margin-top: 50px;
flex-grow: 1;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
}
3、底部固定
1)使用padding加负margin实现底部固定布局
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
height: 100%;
padding-bottom: 50px;
overflow: auto;
box-sizing: border-box;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
height: 100px;
height: 1000px;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
margin-top: -50px;
}
2)使用flex加fixed定位实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
min-height: 100%;
flex-direction:column;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ /* height: 100px; */ height: 1000px;
flex-grow: 1;
margin-bottom: 50px;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
bottom: 0;
}
3、顶底部都固定
1)使用fixed实现顶底部固定布局
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
padding-top: 50px;
padding-bottom: 50px;
/* height: 100px; */ height: 1000px;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
position: fixed;
bottom: 0;
width: 100%;
}
2)使用flex加fixed定位实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="header">header</div>
<div class="content">content</div>
<div class="footer">footer</div>
</div>
html, body {
height: 100%;
margin: 0;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
min-height: 100%;
flex-direction:column;
}
.header {
height: 50px;
background: lightblue;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
}
.content {
background: lightpink;
/* 这里的高度只是为了模拟内容多少 */ /* height: 100px; */ height: 1000px;
flex-grow: 1;
margin-bottom: 50px;
margin-top: 50px;
}
.footer {
height: 50px;
background: lightgreen;
position: fixed;
width: 100%;
bottom: 0;
}
四、两栏布局
两栏布局就是一边固定,另外一边自适应,效果如下:

实现两栏布局的方法也有很多,笔者接下来介绍用的比较多的几种方式:
1、左 float,然后右 margin-left(右边自适应)
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
div {
height: 500px;
}
.aside {
width: 300px;
float: left;
background: yellow;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
margin-left: 300px;
}
2、右 float,然后右 margin-right(左边自适应)
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
div {
height: 500px;
}
.aside {
width: 300px;
float: right;
background: yellow;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
margin-right: 300px;
}
3、absolute定位加margin-left(右边自适应)
<div class="wrap">
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
div {
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
position: relative;
}
.aside {
width: 300px;
background: yellow;
position: absolute;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
margin-left: 300px;
}
4、absolute定位加margin-right(左边自适应)
<div class="wrap">
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
div {
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
position: relative;
}
.aside {
width: 300px;
background: yellow;
position: absolute;
right: 0;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
margin-right: 300px;
}
5、使用flex实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
div {
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
}
.aside {
flex: 0 0 300px;
background: yellow;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
flex: 1 1;
}
6、使用grid实现
<div class="wrap">
<div class="aside"></div>
<div class="main"></div>
</div>
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 300px auto;
}
.aside {
background: yellow;
}
.main {
background: aqua;
}
六、三栏布局
三栏布局就是两边固定,中间自适应布局,效果如下:

实现三栏布局的方法也有很多,笔者接下来介绍用的比较多的几种方式:
1、position + margin-left + margin-right实现三栏布局
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
div {
height: 500px;
}
.left {
position: absolute;
left: 0;
top: 0;
width: 200px;
background: green;
}
.right {
position: absolute;
right: 0;
top: 0;
width: 200px;
background: red;
}
.middle {
margin-left: 200px;
margin-right: 200px;
background: lightpink;
}
2、float + margin-left + margin-right实现三栏布局
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
div {
height: 500px;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
background: green;
float: left;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
background: yellow;
float: right;
}
.middle {
margin-left: 200px;
margin-right: 200px;
background: lightpink;
}
3、flex实现三栏布局
<div class="wrap">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
div {
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
display: flex;
}
.left {
flex: 0 0 200px;
background: green;
}
.right {
flex: 0 0 200px;
background: yellow;
}
.middle {
background: lightpink;
flex: 1 1;
}
4、grid实现三栏布局
<div class="wrap">
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="middle"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</div>
html,
body {
margin: 0;
}
div {
height: 500px;
}
.wrap {
display: grid;
grid-template-columns: 200px auto 200px;
}
.left {
background: green;
}
.right {
background: yellow;
}
.middle {
background: lightpink;
}
七、圣杯布局
圣杯布局在项目中基本上不会再使用了,在面试中我们会经常碰到,所以需要了解。
主要用到了浮动和和相对定位。
1、html
<div class="container">
<div class="content">中间内容</div>
<div class="left">左侧区域</div>
<div class="right">右侧区域</div>
</div>
2、css
div {
height: 500px;
}
.container {
padding: 0 200px 0 200px;
border: 1px solid black;
}
.content {
float: left;
width: 100%;
background: #f00;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
background: #0f0;
float: left;
margin-left: -100%;
position: relative;
left: -200px;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
background: #00f;
float: left;
margin-left: -200px;
position: relative;
right: -200px;
}
八、双飞翼布局
双飞翼布局在项目中基本上不会再使用了,在面试中我们会经常碰到,所以需要了解。
主要用到了浮动。
1、html
<div class="main">
<div class="content">content</div>
</div>
<div class="left">left</div>
<div class="right">right</div>
2、css
div {
height: 500px;
}
.main {
float: left;
width: 100%;
background: #f00;
}
.main .content {
/* margin、padding这两种方式都可以 */
/* margin-left: 200px;
margin-right: 300px; */ padding-left: 200px;
padding-right: 300px;
}
.left {
width: 200px;
background: #0f0;
float: left;
margin-left: -100%;
}
.right {
width: 200px;
background: #00f;
float: left;
margin-left: -200px;
}
九、总结
因为flex和grid布局方法已经很强大了,日常工作中99%的布局都可以使用这两种方式来实现。所以笔者建议能使用flex或者grid布局方法实现的就尽量使用这两种布局方式实现。因为不仅简单而且负面作用也很少。
浮动布局和绝对定位布局会导致元素脱离文档流,会带来一些负面作用,有时会导致一些意想不到的结果。
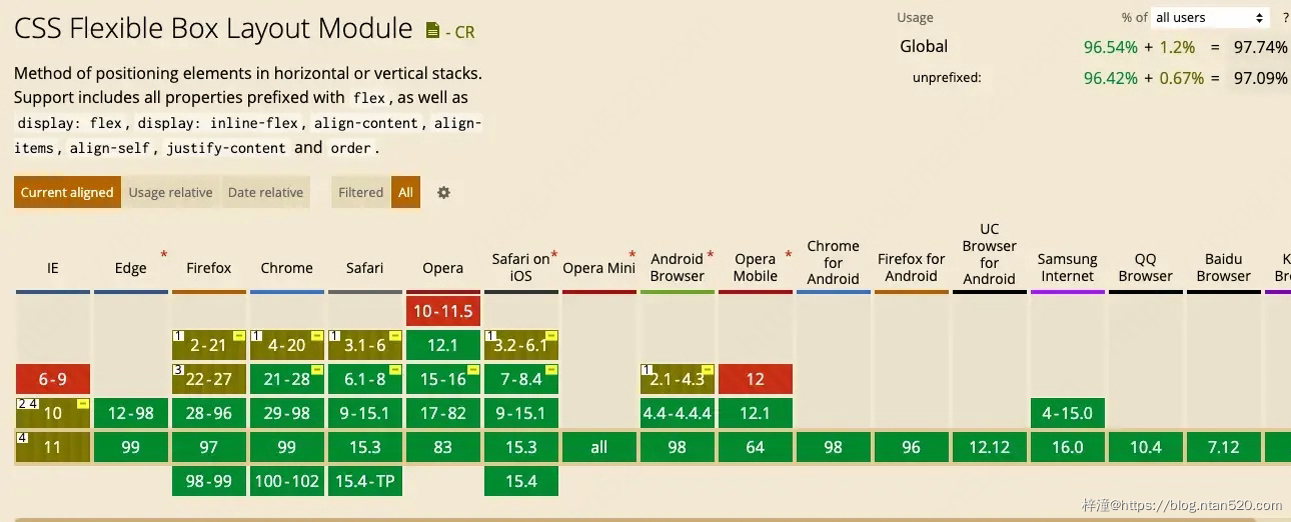
关于flex布局的兼容性和grid布局的兼容性,目前已经支持的很好了,大家可以放心使用。
1、flex布局的兼容性
2、grid布局的兼容性

