文章内容
1、注解定义
定义两个注解 @Decrypt 和 @Encrypt:
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.PARAMETER})
public @interface Decrypt {
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface Encrypt {
}
这两个注解就是两个标记,在以后使用的过程中,哪个接口方法添加了 @Encrypt 注解就对哪个接口的数据加密返回,哪个接口/参数添加了 @Decrypt 注解就对哪个接口/参数进行解密。需要注意的是 @Decrypt 比 @Encrypt 多了一个使用场景就是 @Decrypt 可以用在参数上。
2、配置类
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.encrypt")
public class EncryptProperties {
private final static String DEFAULT_KEY = "blog.ntan520.com";
private String key = DEFAULT_KEY;
public String getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(String key) {
this.key = key;
}
}
这里设置了默认的 key 是 blog.ntan520.com,key 是 16 位字符串。以后如果想配置 key,只需要在 application.properties 中配置 spring.encrypt.key=xxx 即可。
3、使用ResponseBodyAdvice和RequestBodyAdvice实现加解密
参照:RequestBodyAdvice和ResponseBodyAdvice在SpringMVC项目中的使用
ResponseBodyAdvice在使用了@ResponseBody注解的时候才会生效,RequestBodyAdvice在使用了@RequestBody注解的时候才会生效。换言之,前后端都是JSON交互的时候,这两个才有用。不过一般来说接口加解密的场景也都是前后端分离的时候才可能有的事。
1)接口加密:
@EnableConfigurationProperties(EncryptProperties.class)
@ControllerAdvice
public class EncryptResponse implements ResponseBodyAdvice<Result> {
private ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
@Autowired
EncryptProperties encryptProperties;
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter returnType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return returnType.hasMethodAnnotation(Encrypt.class);
}
@Override
public RespBean beforeBodyWrite(RespBean body, MethodParameter returnType, MediaType selectedContentType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> selectedConverterType, ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response) {
byte[] keyBytes = encryptProperties.getKey().getBytes();
try {
if (body.getMessage()!=null) {
body.setMessage(AESUtils.encrypt(body.getMessage().getBytes(), keyBytes));
}
if (body.getData() != null) {
body.setData(AESUtils.encrypt(om.writeValueAsBytes(body.getData()), keyBytes));
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return body;
}
}
这里自定义EncryptResponse类实现 ResponseBodyAdvice 接口,泛型表示接口的返回类型,这里一共要实现两个方法:
- supports:这个方法用来判断什么样的接口需要加密,参数 returnType 表示返回类型,我们这里的判断逻辑就是方法是否含有 @Encrypt 注解,如果有,表示该接口需要加密处理,如果没有,表示该接口不需要加密处理。
- beforeBodyWrite:这个方法会在数据响应之前执行,也就是我们先对响应数据进行二次处理,处理完成后,才会转成 json 返回。我们这里的处理方式很简单,Result中的 status 是状态码就不用加密了,另外两个字段重新加密后重新设置值即可。Result参照:Java接口统一返回数据结构封装
- 另外需要注意,自定义的ResponseBodyAdvice需要用@ControllerAdvice注解来标记。
2)接口解密:
@EnableConfigurationProperties(EncryptProperties.class)
@ControllerAdvice
public class DecryptRequest extends RequestBodyAdviceAdapter {
@Autowired
EncryptProperties encryptProperties;
@Override
public boolean supports(MethodParameter methodParameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) {
return methodParameter.hasMethodAnnotation(Decrypt.class) || methodParameter.hasParameterAnnotation(Decrypt.class);
}
@Override
public HttpInputMessage beforeBodyRead(final HttpInputMessage inputMessage, MethodParameter parameter, Type targetType, Class<? extends HttpMessageConverter<?>> converterType) throws IOException {
byte[] body = new byte[inputMessage.getBody().available()];
inputMessage.getBody().read(body);
try {
byte[] decrypt = AESUtils.decrypt(body, encryptProperties.getKey().getBytes());
final ByteArrayInputStream bais = new ByteArrayInputStream(decrypt);
return new HttpInputMessage() {
@Override
public InputStream getBody() throws IOException {
return bais;
}
@Override
public HttpHeaders getHeaders() {
return inputMessage.getHeaders();
}
};
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return super.beforeBodyRead(inputMessage, parameter, targetType, converterType);
}
}
注意:DecryptRequest 类没有直接实现 RequestBodyAdvice 接口,而是继承自 RequestBodyAdviceAdapter 类,该类是 RequestBodyAdvice 接口的子类,并且实现了接口中的一些方法,这样当继承自 RequestBodyAdviceAdapter 时,就只需要根据自己实际需求实现某几个方法即可。
- supports:该方法用来判断哪些接口需要处理接口解密,这里的判断逻辑是方法上或者参数上含有 @Decrypt 注解的接口,处理解密问题。
- beforeBodyRead:这个方法会在参数转换成具体的对象之前执行,先从流中加载到数据,然后对数据进行解密,解密完成后再重新构造 HttpInputMessage 对象返回。
4、自动化配置类
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.ntan520" })
public class EncryptApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(EncryptApplication.class, args);
}
}
5、application.properties配置文件
spring.encrypt.key=blog.ntan520.com
6、注解使用
1)实体类:
public class User implements Response {
private Long id;
private String username;
//省略 getter/setter
}
2)测试接口:
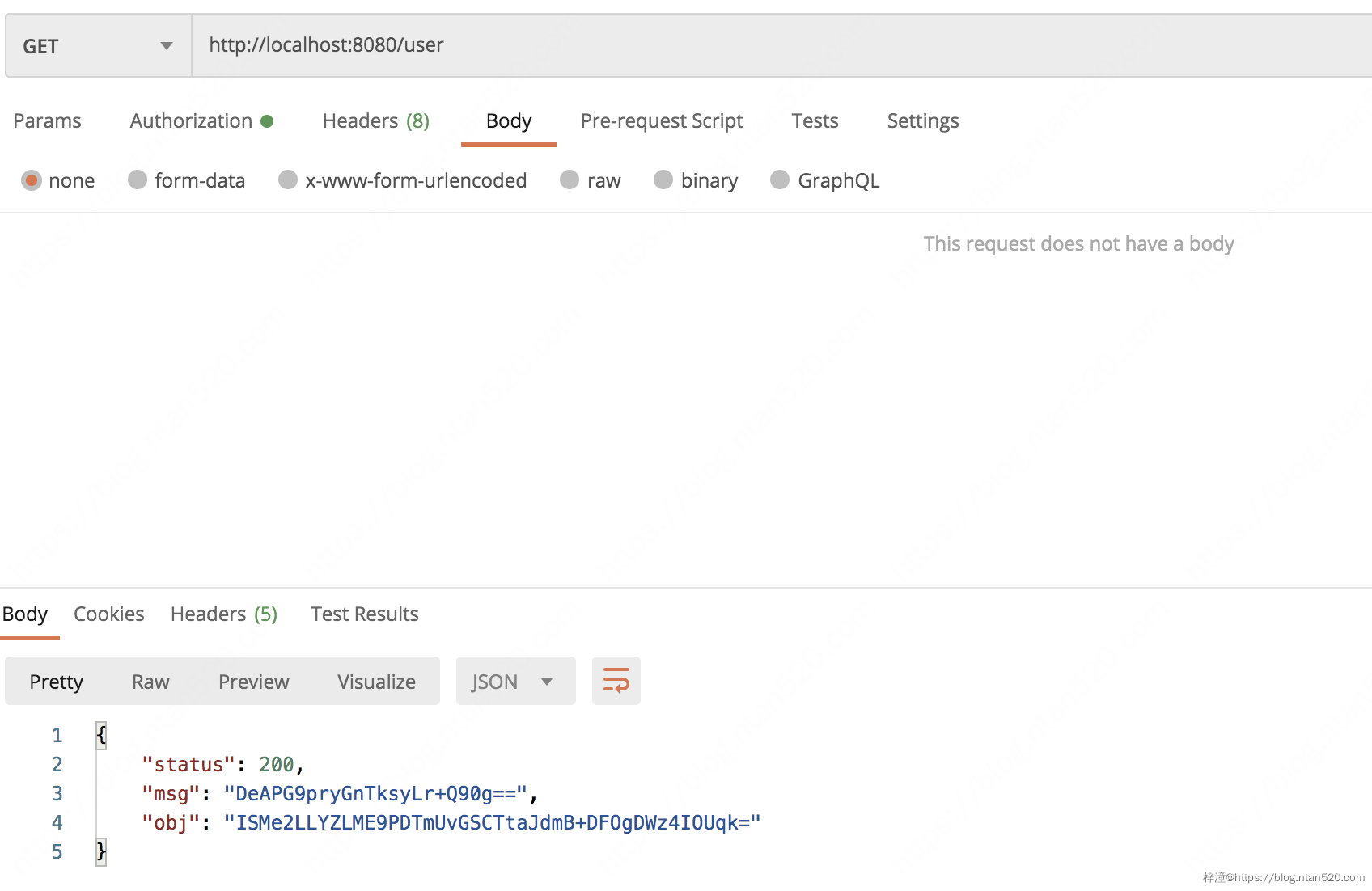
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/user")
@Encrypt
public Result getUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setId(99L);
user.setUsername("nick");
return Result.instance(user);
}
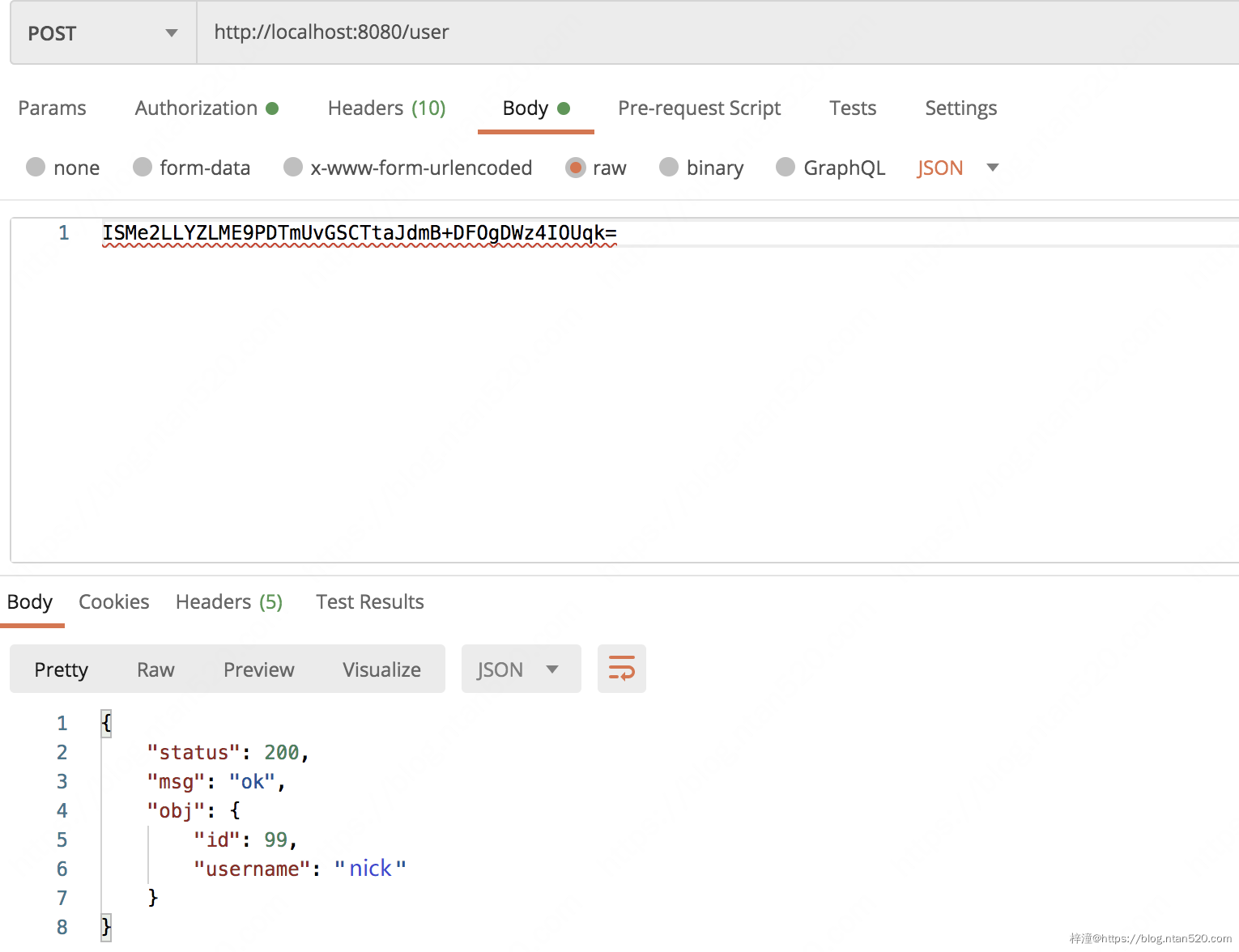
@PostMapping("/user")
public Result addUser(@RequestBody @Decrypt User user) {
System.out.println("user = " + user);
return Result.instance(user);
}
}
第一个接口使用了 @Encrypt 注解,所以会对该接口的数据进行加密(如果不使用该注解就不加密),第二个接口使用了 @Decrypt 所以会对上传的参数进行解密,注意 @Decrypt 注解既可以放在方法上也可以放在参数上。
7、测试
1)测试GET请求接口:
2)测试POST请求接口: