文章内容
计算机领域有人说过一句名言:“计算机科学领域的任何问题都可以通过增加一个中间层来解决”,本文使用Spring-cache给网站添加一层缓存,让网站速度飞起来。
一、Spring Cache介绍
Spring 3.1引入了基于注解的缓存(cache)技术,它本质上是一个对缓存使用的抽象,通过在既有代码中添加少量它定义的各种注解,就能够达到缓存方法的效果。
Spring Cache接口为缓存的组件规范定义,包含缓存的各种操作集合,并提供了各种xxxCache的实现,如RedisCache,EhCacheCache,ConcurrentMapCache等;
项目整合Spring Cache后每次调用需要缓存功能的方法时,Spring会检查检查指定参数的指定的目标方法是否已经被调用过,如果有就直接从缓存中获取结果,没有就调用方法并把结果放到缓存。
二、缓存注解介绍
对于缓存声明,Spring的缓存提供了一组java注解:
- @CacheConfig:设置类级别上共享的一些常见缓存设置。
- @Cacheable:触发缓存写入。
- @CacheEvict:触发缓存清除。
- @Caching:将多种缓存操作分组
- @CachePut:更新缓存(不会影响到方法的运行)。
1、@CacheConfig
该注解是可以将缓存分类,它是类级别的注解方式。可以这么使用它。这样的话,UserServiceImpl的所有缓存注解例如@Cacheable的value值就都为user。
@CacheConfig(cacheNames = "user")
@Service
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {}
2、@Cacheable
一般用于查询操作,根据key查询缓存。
- 如果key不存在,查询db,并将结果更新到缓存中。
- 如果key存在,直接查询缓存中的数据。
//查询数据库后 数据添加到缓存
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser(Integer id) {
return repository.getUser(id);
}
3、@CachePut
@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
//修改数据后更新缓存
@Override
@CachePut(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#updateUser.id", unless = "#result == null")
public User updateUser(User updateUser) {
return repository.save(updateUser);
}
4、@CacheEvict
根据key删除缓存中的数据。allEntries=true表示删除缓存中的所有数据。
//清除一条缓存,key为要清空的数据
@Override
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#id")
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
repository.deleteById(id);
}
5、@Caching
能够为一个提供多个缓存配置,用于定制复杂的缓存规则。
@Caching(
cacheable = {
@Cacheable(value = "emp",key = "#lastName")
},
put = {
@CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.id"),
@CachePut(value = "emp",key = "#result.email"),
}
)
三、Spring Boot+Cache示例
1、pom.xml引入jar包
<!-- 引入缓存 starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-cache</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 引入 redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、启动类添加@EnableCaching注解
@EnableCaching注解是spring framework中的注解驱动的缓存管理功能,当你在配置类(@Configuration)上使用@EnableCaching注解时,会触发一个post processor,这会扫描每一个spring bean,查看是否已经存在注解对应的缓存。如果找到了,就会自动创建一个代理拦截方法调用,使用缓存的bean执行处理。
启动类部分代码如下:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableCaching
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
3、配置数据库和redis连接
application.properties部分配置如下:
#配置数据源信息
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://192.168.1.1:3306/test
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=1234
#配置jpa
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.jpa.show-sql=true
spring.jackson.serialization.indent_output=true
# Redis服务器地址
spring.redis.host=192.168.1.1
# database
spring.redis.database = 1
# Redis服务器连接端口 使用默认端口6379可以省略配置
spring.redis.port=6379
# Redis服务器连接密码(默认为空)
spring.redis.password=1234
# 连接池最大连接数(如果配置<=0,则没有限制 )
spring.redis.jedis.pool.max-active=8
4、配置CacheManager
WebConfig.java部分配置如下:
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
//缓存配置对象
RedisCacheConfiguration redisCacheConfiguration = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig();
redisCacheConfiguration = redisCacheConfiguration.entryTtl(Duration.ofMinutes(30L)) //设置缓存的默认超时时间:30分钟
.disableCachingNullValues() //如果是空值,不缓存
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(keySerializer())) //设置key序列化器
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer((valueSerializer()))); //设置value序列化器
return RedisCacheManager
.builder(RedisCacheWriter.nonLockingRedisCacheWriter(redisConnectionFactory))
.cacheDefaults(redisCacheConfiguration).build();
}
5、使用缓存注解
UserServiceImpl.java中使用缓存注解示例如下:
//查询数据库后 数据添加到缓存
@Override
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#id", unless = "#result == null")
public User getUser(Integer id) {
return repository.getUser(id);
}
//清除一条缓存,key为要清空的数据
@Override
@CacheEvict(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#id")
public void deleteUser(Integer id) {
repository.deleteById(id);
}
//修改数据后更新缓存
@Override
@CachePut(cacheNames = "cacheManager", key = "'USER:'+#updateUser.id", unless = "#result == null")
public User updateUser(User updateUser) {
return repository.save(updateUser);
}
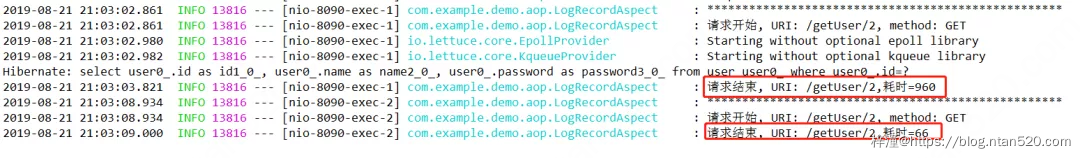
6、查看缓存效果
启动服务后,访问两次http://localhost:8090/getUser/2接口,从打印日志可以看到,第一次请求打印了sql说明查询了数据库,耗时960,而第二次直接查询的缓存耗时66,增加缓存后速度提升非常明显。

四、注意事项
Spring cache是基于Spring Aop来动态代理机制来对方法的调用进行切面,这里关键点是对象的引用问题,如果对象的方法是内部调用(即 this 引用)而不是外部引用,则会导致 proxy 失效,那么切面就失效,也就是说上面定义的各种注释包括 @Cacheable、@CachePut 和 @CacheEvict 都会失效。
